California SNOW REPORT
April 15 2024
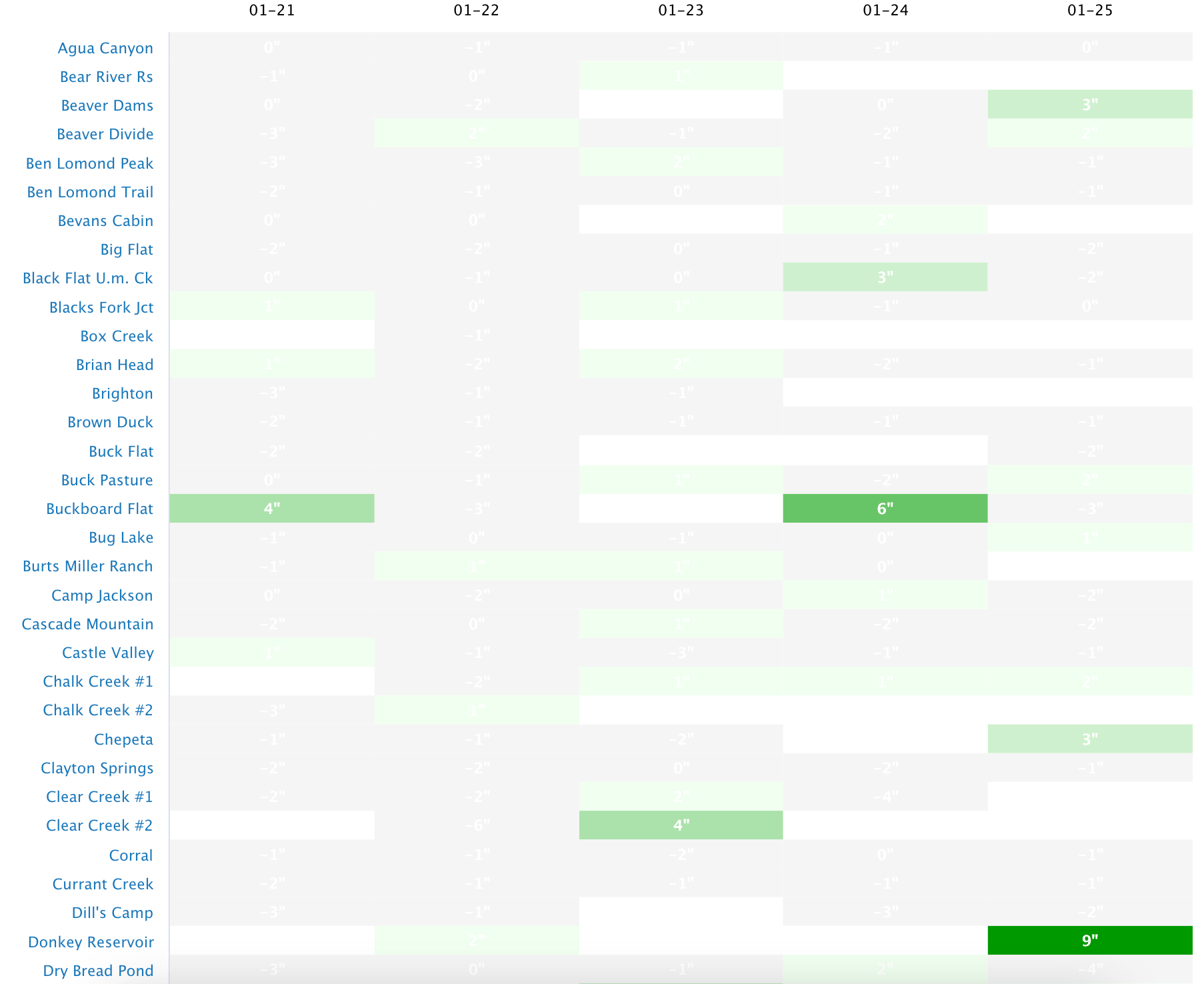
California's snowpack displays a varied landscape across different regions, with some areas boasting substantial depths, while others face shortages, leaving snow enthusiasts with select options for winter recreation. While the high elevations, such as Leavitt Lake with a snowpack depth of 145 inches, and areas within the vicinity of major ski resorts like Mammoth Pass, which reports a depth of 102.8 inches, are in good condition for skiing and snowboarding, lower elevation sites like Independence Lake (25 inches) and Tahoe City Cross (22 inches) are experiencing thinner snowpacks. Noteworthy is the impressive snowfall in the last 24 hours at Casa Vieja Meadows near the southern Sierra Nevada, with 25.5 inches, suggesting excellent fresh snow conditions for backcountry activities.
The recent snowfall also benefits the well-known Palisades Tahoe ski area, which received 2 inches of new snow, reinforcing an already satisfactory base depth of 68 inches. However, it's clear that ...
California's snowpack displays a varied landscape across different regions, with some areas boasting substantial depths, while others face shortages, leaving snow enthusiasts with select options for winter recreation. While the high elevations, such as Leavitt Lake with a snowpack depth of 145 inches, and areas within the vicinity of major ski resorts like Mammoth Pass, which reports a depth of 102.8 inches, are in good condition for skiing and snowboarding, lower elevation sites like Independence Lake (25 inches) and Tahoe City Cross (22 inches) are experiencing thinner snowpacks. Noteworthy is the impressive snowfall in the last 24 hours at Casa Vieja Meadows near the southern Sierra Nevada, with 25.5 inches, suggesting excellent fresh snow conditions for backcountry activities.
The recent snowfall also benefits the well-known Palisades Tahoe ski area, which received 2 inches of new snow, reinforcing an already satisfactory base depth of 68 inches. However, it's clear that no significant snowfall is expected in the next five days across the state, indicating that current snowpack levels are stable for the immediate future. This could be a concern for areas already facing deficits, as diminished snowpacks could affect not only winter sports but also water supply come spring and summer.
Lastly, winter sports enthusiasts are encouraged to seek higher elevations for more reliable conditions, as the current snowpack trends show these areas are most likely to provide the desired snowy landscapes. Despite the lack of incoming storms, the existing snowpack at higher altitudes, especially in the Sierra Nevada range, maintains ample opportunities for snow-based activities, although visitors should remain aware of local conditions and potential variations in snowpack stability. Overall, the state's snowpack is a mixed bag, but with careful planning, there is still ample winter joy to be found on California's snowy peaks.
Snowpack conditions in California vary across different mountain ranges that supply snow for the state's water resources. The Sierra Nevada range is a crucial source, with snowpack providing nearly one-third of the state's water supply. The snowpack in the Sierra Nevada is measured by the California Department of Water Resources via manual surveys and electronic sensors known as snow telemetry (SNOTEL) sites. Other mountain ranges, such as the Cascades and the Siskiyou Mountains, also contribute to California's snowpack.
Snowpack runoff from these mountains feeds into several important rivers and watersheds, including the Sacramento River, San Joaquin River, and the Colorado River. These watersheds supply water for agriculture, drinking water, and hydroelectric power.
California's winter climate is characterized by periodic storms known as "atmospheric rivers," which bring heavy precipitation and contribute to snow accumulation. However, climate change poses a threat to the state's snowpack, as rising temperatures may lead to more rainfall than snowfall, altering the timing and quantity of water supply.
Interesting facts about snow science and history in California include the development of advanced techniques to measure snowpack, such as airborne laser scanning (LiDAR), which provides detailed information about the snowpack's depth and density. Additionally, the 2015 snowpack was historically low, reaching only 5% of the average due to severe drought conditions. Overall, accurate and up-to-date information on snowpack conditions is crucial for managing California's water resources effectively.


 Snoflo Premium
Snoflo Premium