San Andreas Reservoir Report
Nearby: Spencer Lake Pilarcitos
Last Updated: March 13, 2026
The San Andreas Fault is a major geological feature that runs through California for over 800 miles.
Summary
It is responsible for many earthquakes in the region, including the San Francisco earthquake of 1906. Hydrology in the region is important, as the fault is responsible for creating natural springs and streams that provide water to surrounding areas. Specific surface flow providers include the San Andreas Creek and the San Andreas River. Snowpack providers include the Sierra Nevada Mountains and the Cascade Range. Agriculture is an important use of the land surrounding the fault, with crops such as almonds, avocados, and citrus being grown in the region. Recreational activities include hiking, camping, and fishing in the many parks and wilderness areas surrounding the fault.
°F
°F
mph
Wind
%
Humidity
15-Day Weather Outlook
Reservoir Details
| Storage 24hr Change | -0.04% |
| Percent of Normal | 79% |
| Minimum |
11,172.0 acre-ft
2024-06-05 |
| Maximum |
17,769.0 acre-ft
2023-01-16 |
| Average | 15,614 acre-ft |
| Dam_Height | 107 |
| Hydraulic_Height | 97 |
| Drainage_Area | 4.4 |
| Year_Completed | 1870 |
| Nid_Storage | 19027 |
| Primary_Dam_Type | Earth |
| Surface_Area | 550 |
| Hazard_Potential | High |
| River_Or_Stream | Tr San Mateo Cr |
| Dam_Length | 727 |
| Nid_Height | 107 |
Seasonal Comparison
Storage Levels
Pool Elevation Levels
Top Conserv Storage Levels
Inflow Levels
5-Day Hourly Forecast Detail
Nearby Streamflow Levels
Dam Data Reference
Condition Assessment
SatisfactoryNo existing or potential dam safety deficiencies are recognized. Acceptable performance is expected under all loading conditions (static, hydrologic, seismic) in accordance with the minimum applicable state or federal regulatory criteria or tolerable risk guidelines.
Fair
No existing dam safety deficiencies are recognized for normal operating conditions. Rare or extreme hydrologic and/or seismic events may result in a dam safety deficiency. Risk may be in the range to take further action. Note: Rare or extreme event is defined by the regulatory agency based on their minimum
Poor A dam safety deficiency is recognized for normal operating conditions which may realistically occur. Remedial action is necessary. POOR may also be used when uncertainties exist as to critical analysis parameters which identify a potential dam safety deficiency. Investigations and studies are necessary.
Unsatisfactory
A dam safety deficiency is recognized that requires immediate or emergency remedial action for problem resolution.
Not Rated
The dam has not been inspected, is not under state or federal jurisdiction, or has been inspected but, for whatever reason, has not been rated.
Not Available
Dams for which the condition assessment is restricted to approved government users.
Hazard Potential Classification
HighDams assigned the high hazard potential classification are those where failure or mis-operation will probably cause loss of human life.
Significant
Dams assigned the significant hazard potential classification are those dams where failure or mis-operation results in no probable loss of human life but can cause economic loss, environment damage, disruption of lifeline facilities, or impact other concerns. Significant hazard potential classification dams are often located in predominantly rural or agricultural areas but could be in areas with population and significant infrastructure.
Low
Dams assigned the low hazard potential classification are those where failure or mis-operation results in no probable loss of human life and low economic and/or environmental losses. Losses are principally limited to the owner's property.
Undetermined
Dams for which a downstream hazard potential has not been designated or is not provided.
Not Available
Dams for which the downstream hazard potential is restricted to approved government users.
Area Campgrounds
| Location | Reservations | Toilets |
|---|---|---|
 Dispersed Camping
Dispersed Camping
|
||
 Sweetwood Group Camp
Sweetwood Group Camp
|
||
 Half Moon Bay State Beach
Half Moon Bay State Beach
|
||
 Candlestick RV Park
Candlestick RV Park
|


 San Andreas
San Andreas
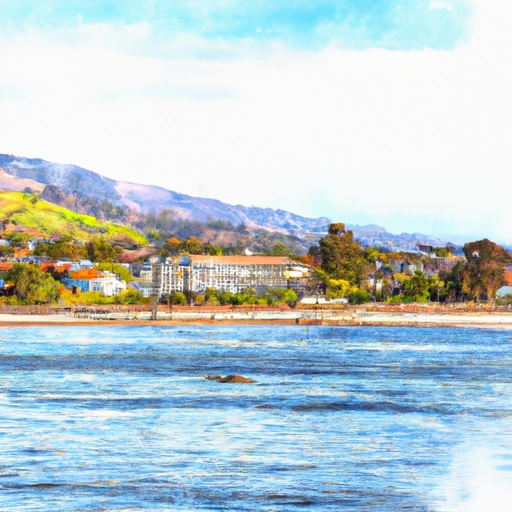 San Andreas
San Andreas
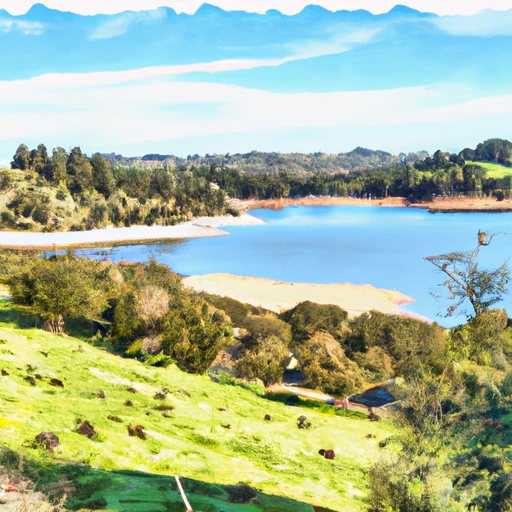 Pilarcitos Lk Nr Hillsborough Ca
Pilarcitos Lk Nr Hillsborough Ca
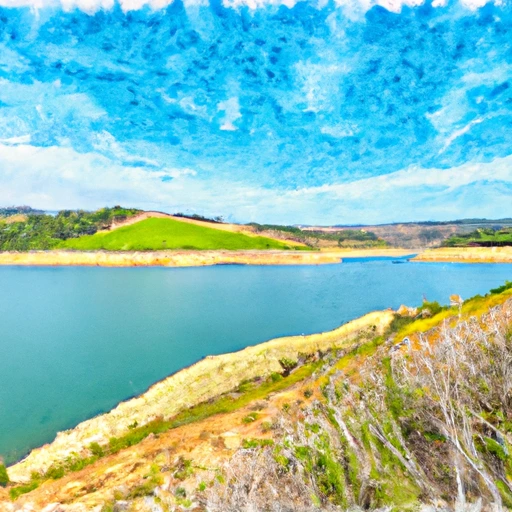 Crystal Sprgs Res A Dam Nr San Mateo Ca
Crystal Sprgs Res A Dam Nr San Mateo Ca
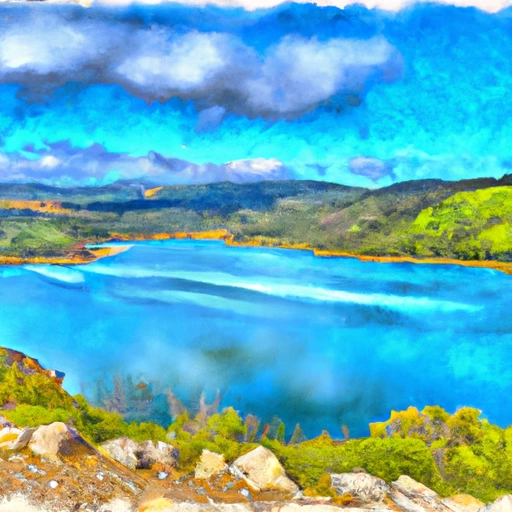 Lower Crystal Springs Reservoir
Lower Crystal Springs Reservoir
 San Andreas Trail San Bruno
San Andreas Trail San Bruno