Oroville Dam Reservoir Report
Last Updated: March 13, 2026
Oroville Dam, located in California, is the tallest dam in the United States and plays a significant role in the state's water supply.
Summary
The dam was completed in 1968 and provides hydroelectric power, flood control, and irrigation water to the surrounding agricultural areas. The dam's reservoir is fed by the Feather River, which in turn is supplied by both surface flow and snowpack from the Sierra Nevada mountains. The reservoir also serves as a recreational area for boating, fishing, and camping. However, in 2017, the dam experienced significant damage during heavy rains, leading to concerns about its safety and necessitating emergency repairs. Despite these concerns, Oroville Dam continues to be an essential component of California's water infrastructure.
°F
°F
mph
Wind
%
Humidity
15-Day Weather Outlook
Reservoir Details
| 24hr Change | None% |
| Percent of Normal | None% |
| Minimum |
|
| Maximum |
|
| Average | |
| Dam_Height | 770 |
| Hydraulic_Height | 748 |
| Drainage_Area | 3611 |
| Year_Completed | 1968 |
| Nid_Storage | 3540000 |
| Structural_Height | 770 |
| Foundations | Rock |
| Surface_Area | 15800 |
| Hazard_Potential | High |
| Outlet_Gates | Tainter (radial) - 8 |
| River_Or_Stream | Feather River |
| Dam_Length | 6920 |
| Primary_Dam_Type | Earth |
| Nid_Height | 770 |
Seasonal Comparison
Storage Levels
Pool Elevation Levels
Top Conserv Storage Levels
Inflow Levels
5-Day Hourly Forecast Detail
Nearby Streamflow Levels
 Butte C Nr Chico Ca
Butte C Nr Chico Ca
|
569cfs |
 Deer C Nr Smartville Ca
Deer C Nr Smartville Ca
|
121cfs |
 Yuba R Nr Marysville Ca
Yuba R Nr Marysville Ca
|
4420cfs |
 N Yuba R Bl Goodyears Bar Ca
N Yuba R Bl Goodyears Bar Ca
|
1110cfs |
 Sacramento R A Colusa Ca
Sacramento R A Colusa Ca
|
10800cfs |
 Bear R Nr Wheatland Ca
Bear R Nr Wheatland Ca
|
13cfs |
Dam Data Reference
Condition Assessment
SatisfactoryNo existing or potential dam safety deficiencies are recognized. Acceptable performance is expected under all loading conditions (static, hydrologic, seismic) in accordance with the minimum applicable state or federal regulatory criteria or tolerable risk guidelines.
Fair
No existing dam safety deficiencies are recognized for normal operating conditions. Rare or extreme hydrologic and/or seismic events may result in a dam safety deficiency. Risk may be in the range to take further action. Note: Rare or extreme event is defined by the regulatory agency based on their minimum
Poor A dam safety deficiency is recognized for normal operating conditions which may realistically occur. Remedial action is necessary. POOR may also be used when uncertainties exist as to critical analysis parameters which identify a potential dam safety deficiency. Investigations and studies are necessary.
Unsatisfactory
A dam safety deficiency is recognized that requires immediate or emergency remedial action for problem resolution.
Not Rated
The dam has not been inspected, is not under state or federal jurisdiction, or has been inspected but, for whatever reason, has not been rated.
Not Available
Dams for which the condition assessment is restricted to approved government users.
Hazard Potential Classification
HighDams assigned the high hazard potential classification are those where failure or mis-operation will probably cause loss of human life.
Significant
Dams assigned the significant hazard potential classification are those dams where failure or mis-operation results in no probable loss of human life but can cause economic loss, environment damage, disruption of lifeline facilities, or impact other concerns. Significant hazard potential classification dams are often located in predominantly rural or agricultural areas but could be in areas with population and significant infrastructure.
Low
Dams assigned the low hazard potential classification are those where failure or mis-operation results in no probable loss of human life and low economic and/or environmental losses. Losses are principally limited to the owner's property.
Undetermined
Dams for which a downstream hazard potential has not been designated or is not provided.
Not Available
Dams for which the downstream hazard potential is restricted to approved government users.
 Bidwell Canyon - Lake Oroville State Rec Area
Bidwell Canyon - Lake Oroville State Rec Area
 Loafer Creek - Lake Oroville State Rec Area
Loafer Creek - Lake Oroville State Rec Area
 Limesaddle - Lake Oroville State Rec Area
Limesaddle - Lake Oroville State Rec Area
 Oroville
Oroville
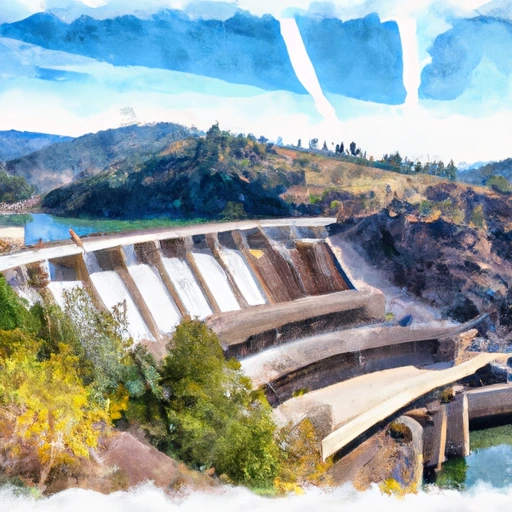 Oroville Dam
Oroville Dam
 Thermalito Diversion Pool
Thermalito Diversion Pool
 Thermalito Total
Thermalito Total
 Thermalito Afterbay
Thermalito Afterbay
 Potters Ravine, Oroville
Potters Ravine, Oroville
 Highway 70 Crossing To Lake Oroville
Highway 70 Crossing To Lake Oroville